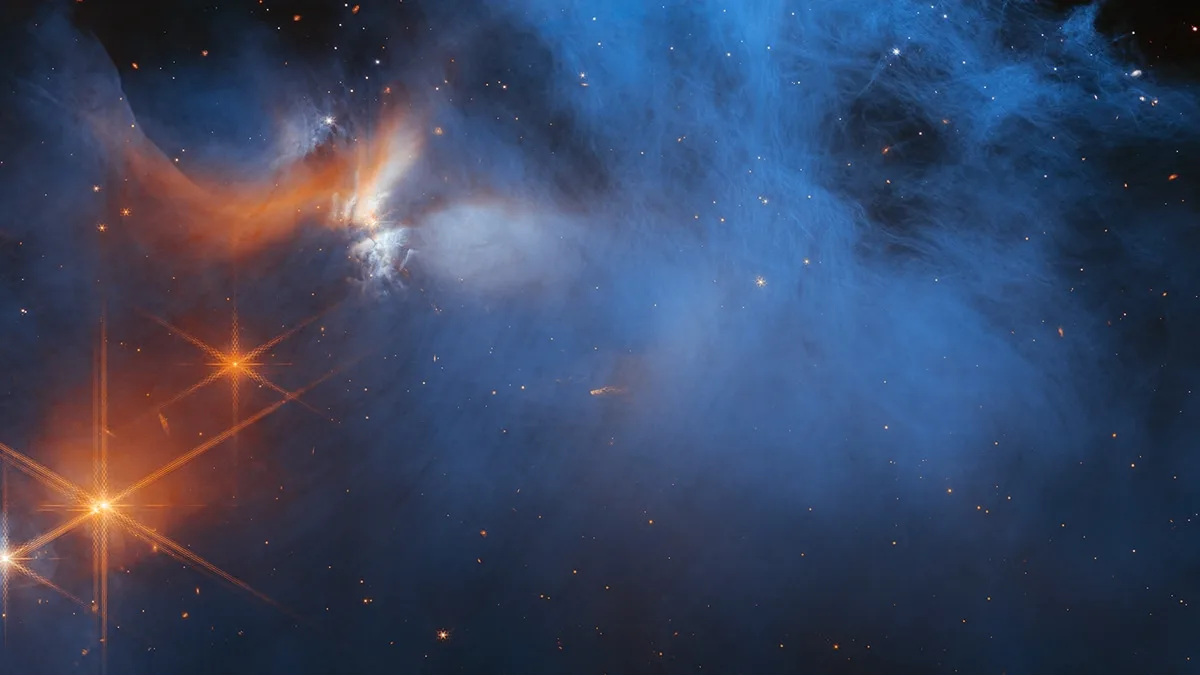
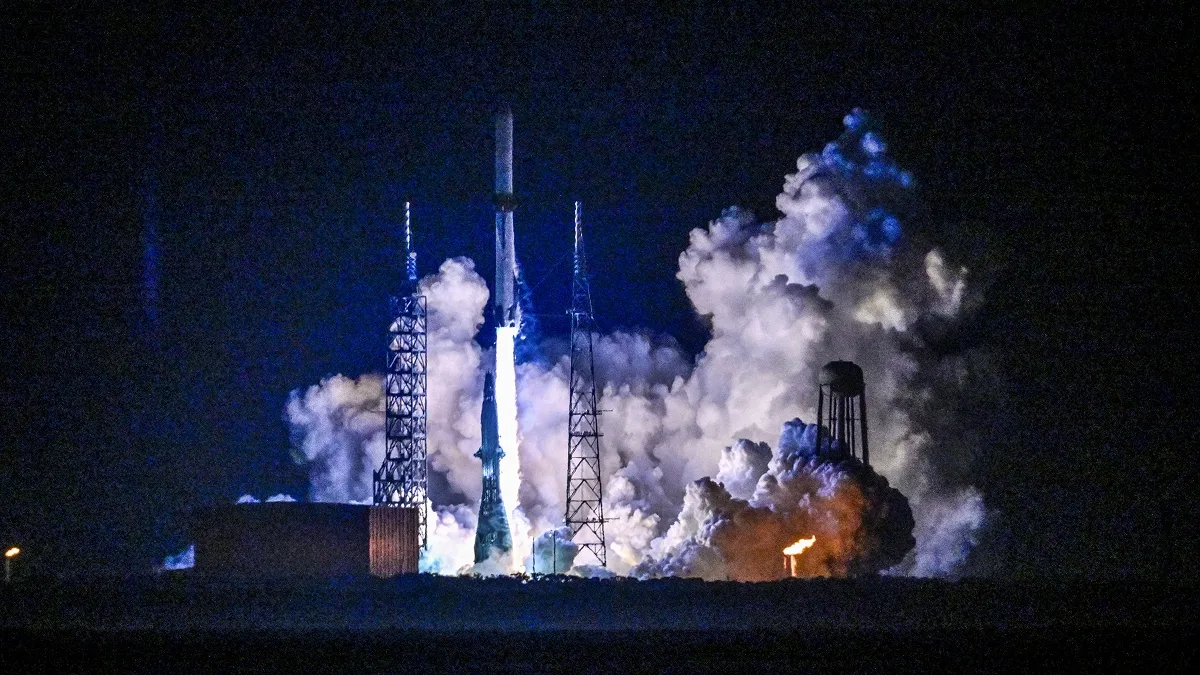
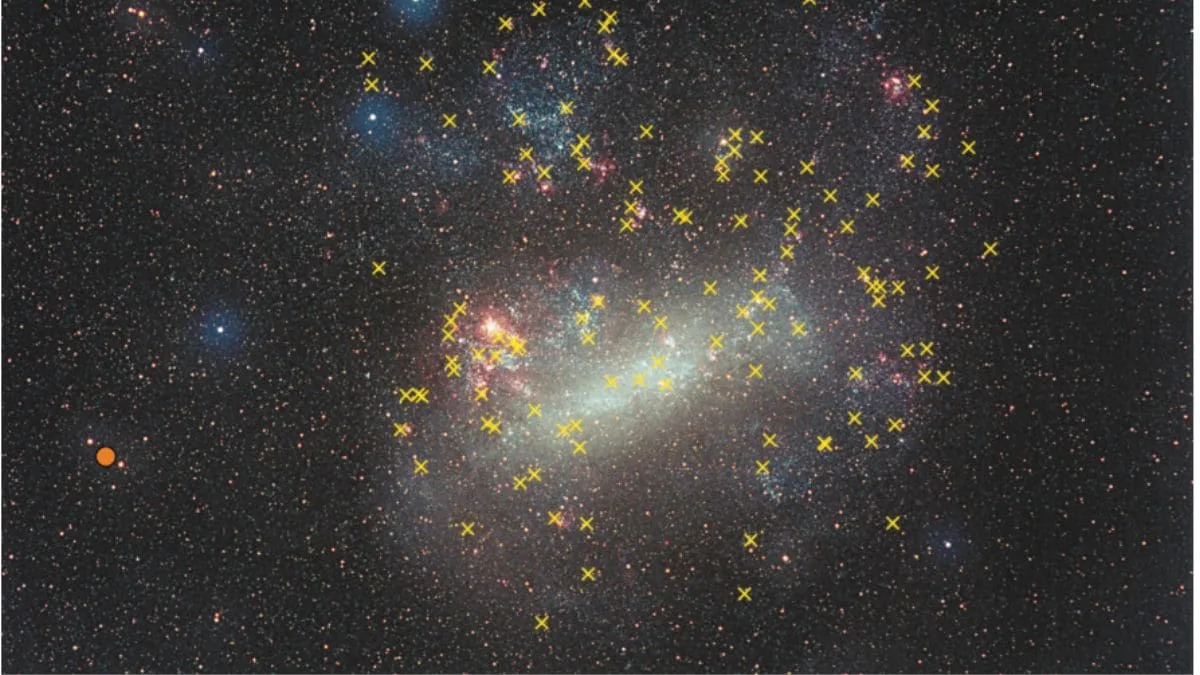
NASA’s SPHEREx mission is set to embark on an extensive survey of the Milky Way, aiming to locate water ice and other essential compounds associated with the formation of life. Slated for launch no earlier than February 27, the spacecraft will be carried into orbit aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force […]